Figure 2
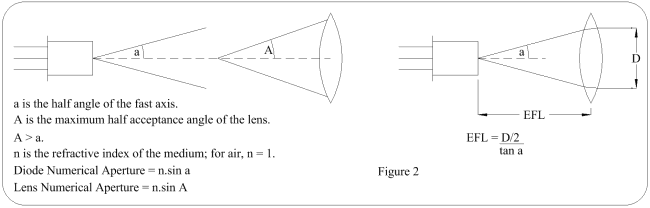
The NA of a lens is a measure of the maximum divergence that the lens can capture from the laser. It is important to note that φ is the half angle of the divergence cone and is given at the marginal ray (not 1/e2 or half max).
Some laser manufacturers give the NA of the source in different terms, such as half max (50% point) or 1/e2 (87% point). Whatever type of number is entered into the formula for the NA of the source will be the same type of number given for the beam diameter. For example, if the half max NA for a laser is used with the above formula, you will get the half max beam diameter. There is no simple way to convert from a half max number or a 1/e2 beam diameter to a full beam diameter for a specific source because it depends on the intensity profile of the source itself. A reasonable approximation, though, for most edge emitting diode lasers is to assume a gaussian beam profile. Using this beam profile, you can convert the beam diameters as follows:
1. To convert a half max beam diameter to a full beam diameter, multiply the diameter by 2.576.
2. To convert a 1/e2 beam diameter to a full beam diameter, multiply the diameter by 1.517.
Ideally, a lens should be used that has an NA higher than the NA of the laser's fast axis. If not, the lens will mask the beam causing some of the light to be wasted.
Referring to Figure 3a:
When b = critical angle: sin b / sin c = nc / nf c = 90° so sin c = 1 sin b = nc / nf sin b = cos d = nc / nf nc / nf = √(1 - sin2d) nc2 = nf2(1 - sin2d) sin a / sin d = nf / na sin2d = na2.sin2a / nf2 nc2 = nf2(1 - na2.sin2a / nf2) nc2 = nf2 - ns2.sin2a sin2a = (nf2 - nc2) / na2 sin a = √[(nf2 - nc2) / na2] = NA For air: sin a = √(nf2 - nc2) = NA So for total internal reflection a < sin-1√(nf2 - nc2)
Previous page: Optics 1
Howard's Stuff Index
Back to Pigeon's Nest
Be kind to pigeons